How Moist and Dry Intrusions Control the Local Hydrologic Cycle in Present and Future Climates
Published in Journal of Climate, 2021
Recommended citation: Smith, S., P. Staten, and J. Lu, 2021: How Moist and Dry Intrusions Control the Local Hydrologic Cycle in Present and Future Climates. Journal of Climate. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0780.1
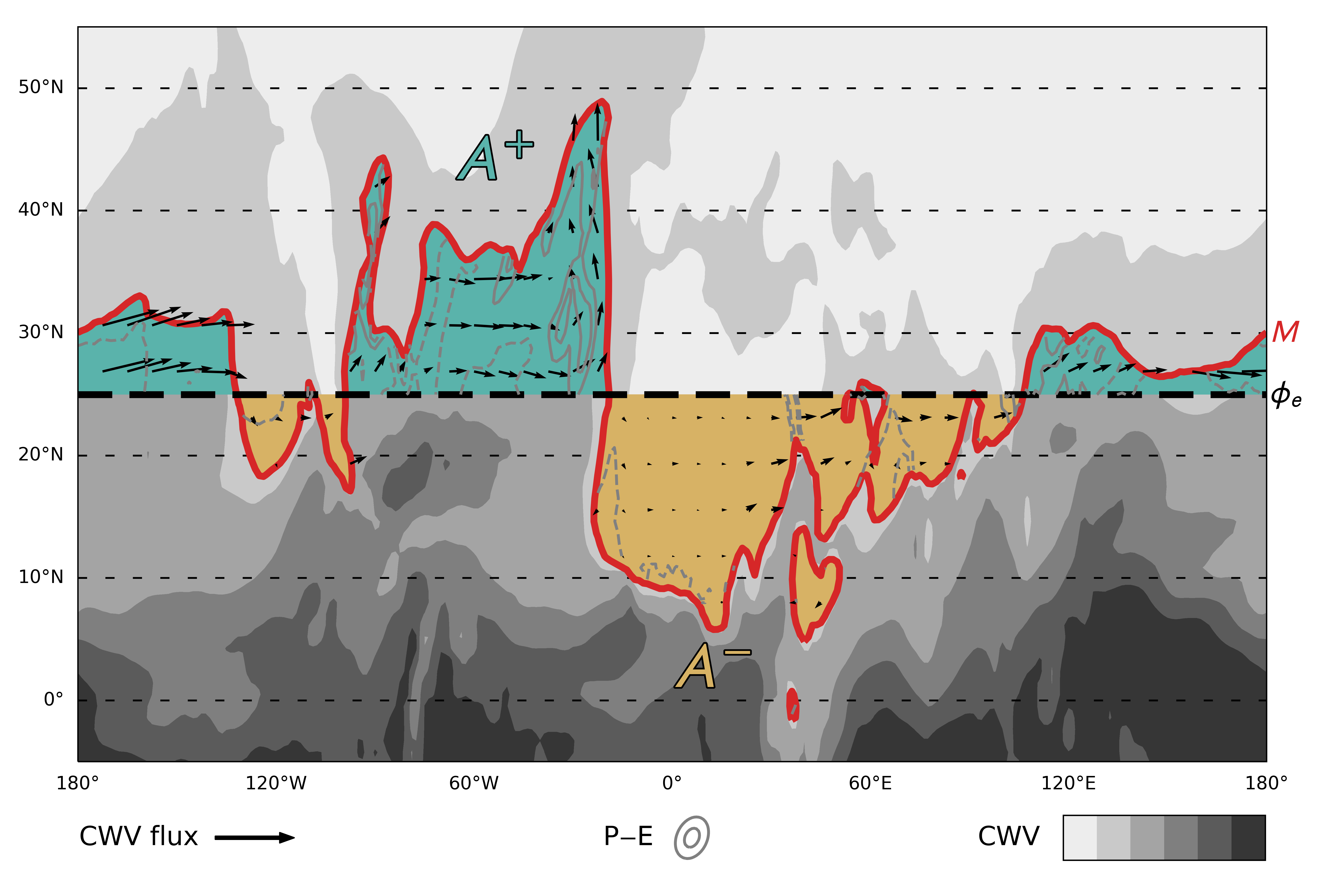
Models disagree on how much the hydrologic cycle could intensify under climate change. These changes are expected to scale with the Clausius–Clapeyron relation but may locally diverge due in part to the uncertain response of the general circulation, causing the hydrologic cycle to inherit this uncertainty. To identify how the circulation contributes, we link circulation changes to changes in the higher moments of the hydrologic cycle using the novel dynamical framework of the local hydrologic cycle, the portion of the hydrologic cycle driven by moist or dry intrusions. We expand this dynamical framework, developing a closed budget that diagnoses thermodynamic, advective, and overturning contributions to future hydrologic cycle changes. In analyzing these changes for the Community Earth System Model Large Ensemble, we show that overturning is the main dynamic contributor to the tropical and subtropical annual response, consistent with a weakening of this circulation. In the extratropics, we show that advective contributions, likely from storm track changes, dominate the response. We achieve a cleaner separation between dynamic and thermodynamic contributions through a semiempirical scaling, which reveals the robustness of the Clausius–Clapeyron scaling for the local hydrologic cycle. This scaling also demonstrates the slowing of the local hydrologic cycle and how changing subtropical dynamics asymmetrically impact wave breaking and suppress meridional moisture transport. We conclude that dynamic changes in the subtropics are predominantly responsible for the annual, dynamic response in the extratropics and thus a significant contributor to uncertainty in future projections.
I am also a co-author on a related paper.
